Definitions
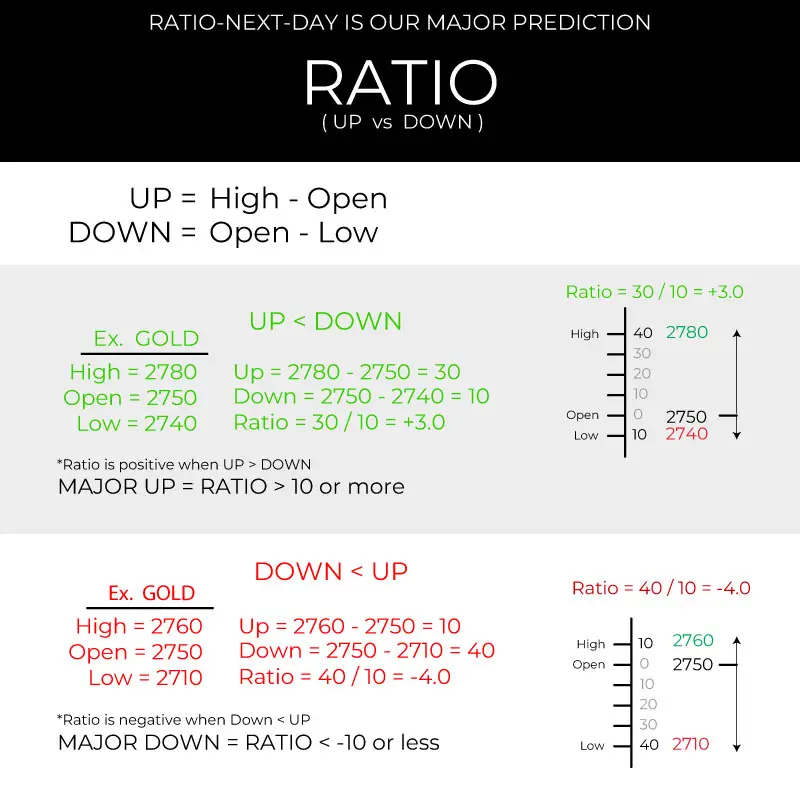
Ratio: (High−Open)/(Open−Low) represents a ratio that compares how far the opening price is from the day’s low to how far the day’s high is from the opening price.
The Significance of Ratio in Trading
The ratio is a metric that provides insights into the price dynamics of a trading day. It is calculated using the formula:
Ratio = (High – Open) / (Open – Low)
What the Ratio Tells Us
A positive ratio indicates that the price moved higher from the opening price, meaning the gap between the open and the high is larger than the gap between the open and the low.
A negative ratio indicates that the price moved lower from the opening price, meaning the gap between the open and the low is larger than the gap between the open and the high.
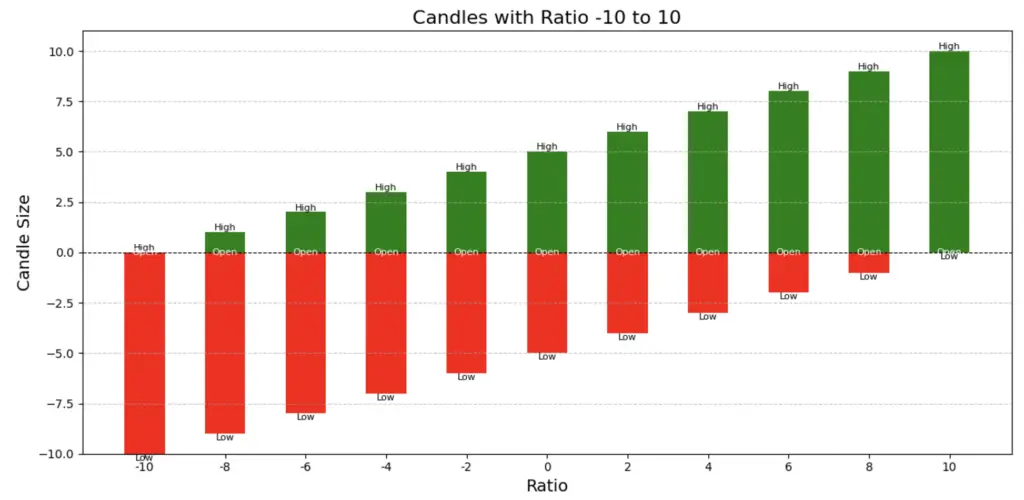
In essence, the ratio reflects the magnitude of price movements in relation to the opening price, providing a snapshot of market sentiment and volatility for the day
Why Predicting Tomorrow’s Ratio is Powerful
Certain days exhibit large ratios, regardless of whether they are positive or negative. On these days, price movements are significant in one direction, offering clear opportunities for strategic trading.
1. Better Risk-to-Reward Opportunities:
A larger ratio implies that potential rewards (price movement in one direction) far outweigh the risks (price movement in the opposite direction).
This creates an ideal scenario for making trades with limited downside risk and substantial upside potential.
2. Actionable Insights for Decision-Making:
By predicting the next day’s ratio, traders can anticipate days with heightened price volatility, enabling them to place more informed and confident bets.
In summary, predicting the next day’s ratio allows us to identify high-opportunity trading days. On these days, we can act decisively to maximize returns while minimizing risk, making ratio a powerful tool for optimizing trading strategies.
Definitions
Close: The price at which the futures contract ends trading on a particular day.
CloseLow (Close – Low): The difference between the closing price and the lowest price of the session.
CloseOpen (Close – Open): This is the difference between the closing price and the opening price.
GapAmt (Gap Amount): The difference between today’s open price and yesterday’s close price.
GapDays: Gaps between the trading days diff (current date – last trading date).
High: The highest price reached by a futures contract during a specific trading session.
HighLow−Open: Represents the percentage range of price movement relative to the opening price in a trading session. This is a measure of volatility and intraday price action in the futures market.
HighOpen (High – Open): This is the difference between the high price of the trading session and the opening price.
HLPercent (High-Low Percent): Is (High-Low)/Open.
Low: The lowest price reached by a futures contract during a specific trading session.
Open: The price at which the futures contract starts trading for the day.
OpenLow (Open – Low): This is the difference between the opening price of the trading session and the Low price.
Ratio: (High−Open)/(Open−Low) represents a ratio that compares how far the opening price is from the day’s low to how far the day’s high is from the opening price.
Relative Volume (7-day and 2-day): The volume of trades over a specific time period relative to the average volume over the last 7 or 2 days.
Volume: Volume represents the total number of contracts traded during the session.